First Aid Training: Emergency Procedures That Work

No one ever wants to be in a situation where they must administer first aid, but accidents happen. It is always best to be prepared for the worst-case scenario. This is why it is crucial to receive proper first aid training.
Emergency Procedures
When an accident occurs, it is crucial to know what emergency procedures to follow. First aid training will teach you how to assess the situation and provide care accordingly properly. It is vital to remain calm in an emergency and remember the steps you learned in training.
Many different types of emergencies can occur, so it is important to be familiar with various procedures.
Heimlich Maneuver
The Heimlich Maneuver is a life-saving technique that can be used to help someone who is choking. The maneuver involves thrusting your fist into the person’s abdomen, which will cause them to expel the object lodged in their throat. The first aid training provider in Edinburgh suggests that Heimlich Maneuver should only be performed on someone choking and unable to speak or breathe. If you are not sure whether or not the person is choking, check for these signs:
- Their face is red or blue.
- They are making a gasping sound.
- They are clutching their throat.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
CPR is an emergency procedure that can be used to save someone who has stopped breathing. It involves chest compressions and rescue breaths. Chest compressions are performed by placing your hands in the center of the person’s chest and pressing down firmly. Rescue breaths are performed by tilting the person’s head back and sealing your mouth over your nose and mouth.
CPR should only be performed on someone unresponsive and not breathing. Here are the steps for performing CPR:
- Check to see if the person is responsive. If they are not responsive, call 911 immediately.
- If the person is responsive, check to see if they are breathing. If they are not breathing, begin CPR by doing chest compressions.
- To do chest compressions, place your hands on each other and press down hard on the center of the person’s chest. You should push down at least 2 inches (5 cm) and no more than 2½ inches (6 cm). Keep pushing down at a rate of 100 compressions per minute.
- After 30 seconds of chest compressions, give two rescue breaths by tilting the victim’s head back and mouth-to-mouth resuscitation until you see their chest rise.
- Repeat steps 3 through 4 until paramedics arrive or the victim begins to breathe on their own.
If you see someone who is not responsive and is not breathing, it is crucial to call 911 immediately and begin CPR. CPR can be the difference between life and death for someone in cardiac arrest. Knowing how to perform CPR could save a life.
Bleeding
Bleeding is a common injury that can happen in several ways. It can result from an accident or an intentional act, such as self-harm. Regardless of the cause, it’s important to know how to stop the bleeding and deal with potential complications.
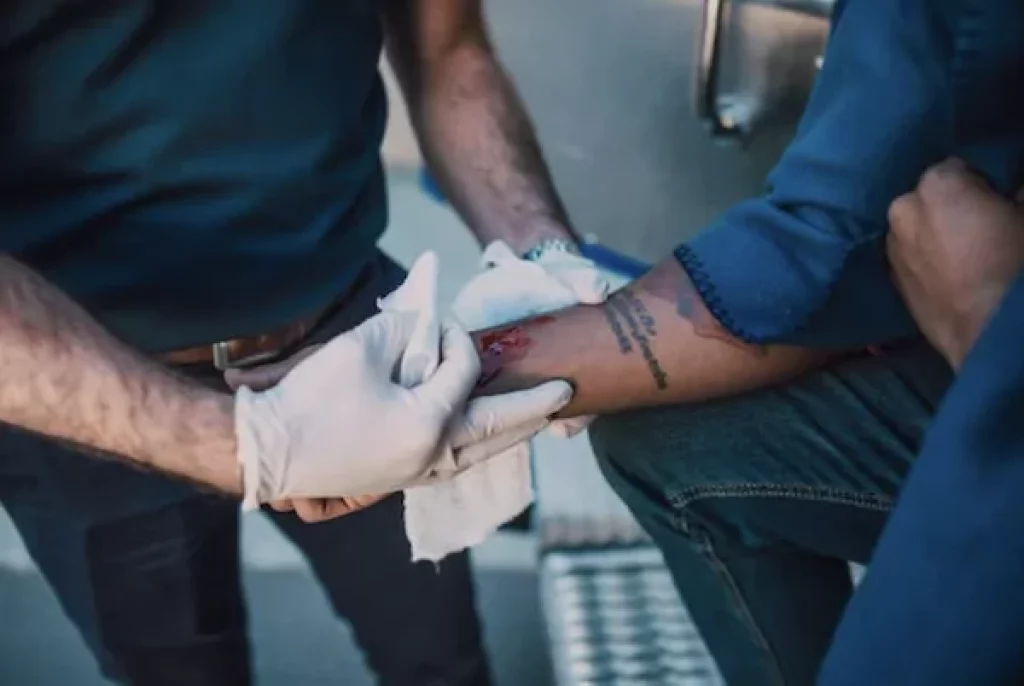
Bleeding from any body part can be dangerous, but some types of bleeding are more severe than others. Arterial bleeding, for example, is characterized by a bright red flow that pulsates with each heartbeat. This bleeding is often difficult to stop and can lead to death if not treated quickly. Venous bleeding, on the other hand, is dark red and flows steadily. It’s less severe than arterial bleeding but still requires treatment. Capillary bleeding is the least serious type of bleeding because it doesn’t flow very much and tends to clot quickly.
How to Stop the Bleeding:
- Apply direct pressure to the wound with a clean cloth or bandage.
- If the bleeding is constant, elevate the limb above the heart level if possible.
- If a limb is wounded, don’t move it unless necessary.
- Apply pressure to any pressure points located between the wound and the heart.
- Call 911 or seek medical help immediately if the bleeding won’t stop.
Burns
Burns are serious injuries that can cause permanent damage if not treated correctly. More than one million people in the United States seek medical treatment for burns each year, and almost half of those cases are due to scalding injuries. Scalding is the most common type of burn, and it occurs when hot liquid or steam comes into contact with the skin. Other causes of burns include flame exposure, contact with hot objects, and electrical injuries.
Burns can be classified according to their severity. The three main categories are first-degree burns, second-degree burns, and third-degree burns. First-degree burns are the least serious and only affect the outer layer of the skin. Second-degree burns affect the outer and inner layers of the skin. Third-degree burns are the most serious and involve all layers of skin as well as underlying tissues such as muscle or bone.
How to Treat a Burn:
- For first-degree and second-degree burns, hold the affected area under cool running water for at least five minutes.
- Remove any jewelry or clothing that is close to the burned area.
- Apply a sterile bandage or clean cloth to the burn.
- Do not apply ice, ointments, or butter to the burn.
- Do not pop any blisters that form.
- If the burn is larger than three inches (seven cm) in diameter or if it is on the face, hands, feet, groin, or buttocks, seek medical help immediately.
Broken Bones
When it comes to broken bones, there are a few things you need to know. First and foremost: not all broken bones are created equal. There are different types of fractures, each with its symptoms and treatment methods. That being said, some general steps can be taken for any fracture, regardless of severity.
First Aid for a Broken Bone:
- If the bone is protruding from the skin, do not touch it. This could cause further damage or infection. Instead, cover the wound with a sterile dressing or wrap it until medical help arrives.
- If possible, immobilize the fracture by splitting it with sticks or other sturdy objects. Ensure the limb is in the correct position before doing so – if you’re unsure how to do this properly, seek medical help immediately.
- Apply ice packs to the fracture area to reduce swelling and pain.
- Keep the victim calm and comfortable until medical help arrives.
Injuries can happen in several ways, and it’s essential to know how to deal with them. This article covers some of the most common injuries – cardiac arrest, bleeding, burns, and broken bones. For each injury, we’ve provided general steps on how to treat it until medical help arrives. Always remember: if you’re unsure what to do, seek medical help immediately.

